“I want my voice to be harsh, I don’t want it to be beautiful, I don’t want it to be pure.” – Frantz Fanon
* The foundation for this writing was gathered from the writings of George Yancy in his book Black Bodies, White Gazes – The continuing significance of race published in 2008
So what am I, a white womxn, doing writing an article on the white gaze when I am not victim to being viewed by the gaze? The answer to this is because it is my attempt to emphasize the importance of this topic to not just people of colour but to white people; to all people. We need to be aware of what it means to be white, what makes a white person “whitely”. (Yancy, 2008: unknown page) and why the white gaze is still prevalent in an apparently liberated society. A person, a body’s sense of identity, imagined community and emphatic identifications is realigned by anti-black racism, according to Linda Martin Alcoff. This article then is a hope towards a more inclusive society, a more woke society even in a “post-apartheid” culture.
In order to unpack the white gaze in a South African context I will look at the photographic work of Alice Mann, Kyle Weeks and Alexia Webster. I am by no means stating that the white gaze is something that is exclusionary to the photographer’s discussed here, they merely serve as examples to aid in a difficult conversation.

Objectifying Black bodies brings to light issues of Black invisibility and hypervisibility as methods of the erasure of the integrity of Black bodies. “The black body is deemed the quintessential object of the ethnographic gaze, the ‘strange’ exotic, and fascinating object of anthropology.” With anthropology, a comradeship was formed with the photographer – anthropologist and photographer worked in unison to document the “strange exotic”.
The apparent social and political emancipation of people of colour that came about through the end of apartheid is bursting at the seams with the narratives of people of colour still frequently lensed by whites that perform their whiteliness through acting out the white gaze.
Employing moral distancing, many white people attain moral superiority over “white racists”. They obscure their own racism by refuting only a specific form of racism thereby creating cavernous self-deception. Hereby is meant that many white people are not self-reflexive enough and only see extremist white supremacy as racist acts while racism gapes far wider than this selected group.
“The white gaze, given the power of the ocular metaphor in Western culture, is an important site of power and control, a site that is structured by white epistemic orders and that perpetuates such orders in turn.” (Yancy, 2008: unknown page) Here is where my argument lies, not in the ocular as a metaphor, but as a definitive object that objectifies in the hands and with the eyes of many a white photographer – something that has been happening since the invention of the camera and still endures.

White people inherited the privilege of being “lookers”, gazers and the power that comes with this state of being. White people assumed the right to appoint Black bodies as they pleased. White hubris then arrogantly takes it upon itself to define the “reality” of people of colour in categorical terms, conditions, stipulations and appellations that are based on white privilege and power.
Veiling their own whiteness, hiding behind their cameras, commodifying from one-dimensional views of Blackness, many white photographers have assisted in creating and maintaining distorted conceptions of Blackness.
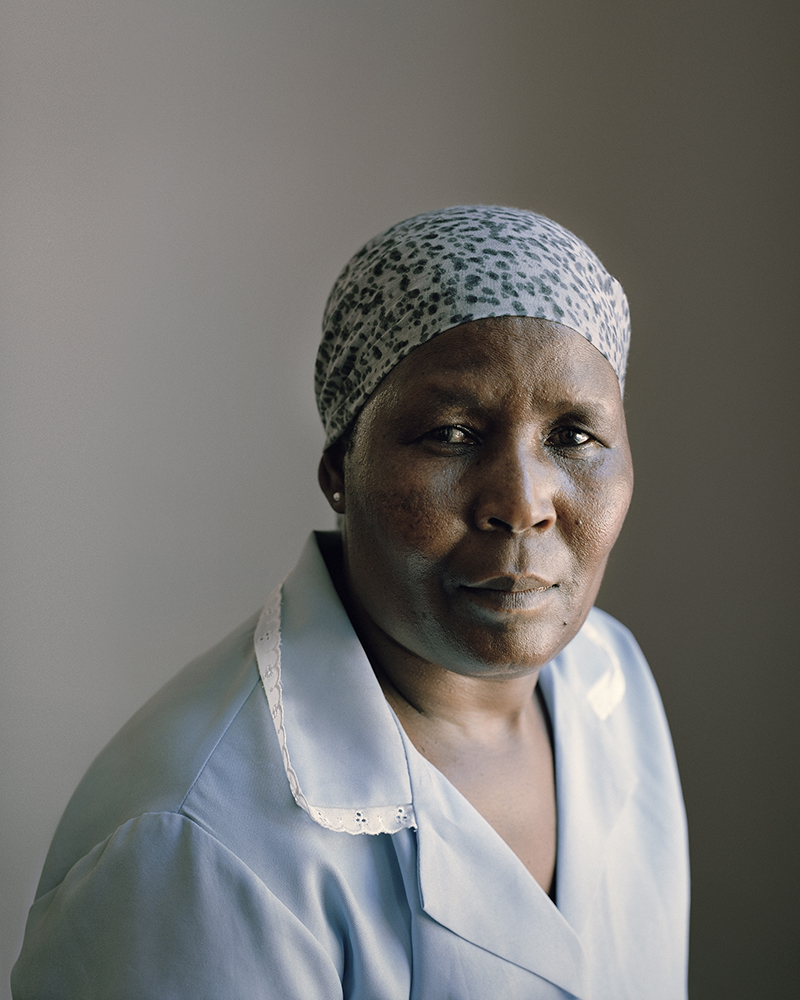
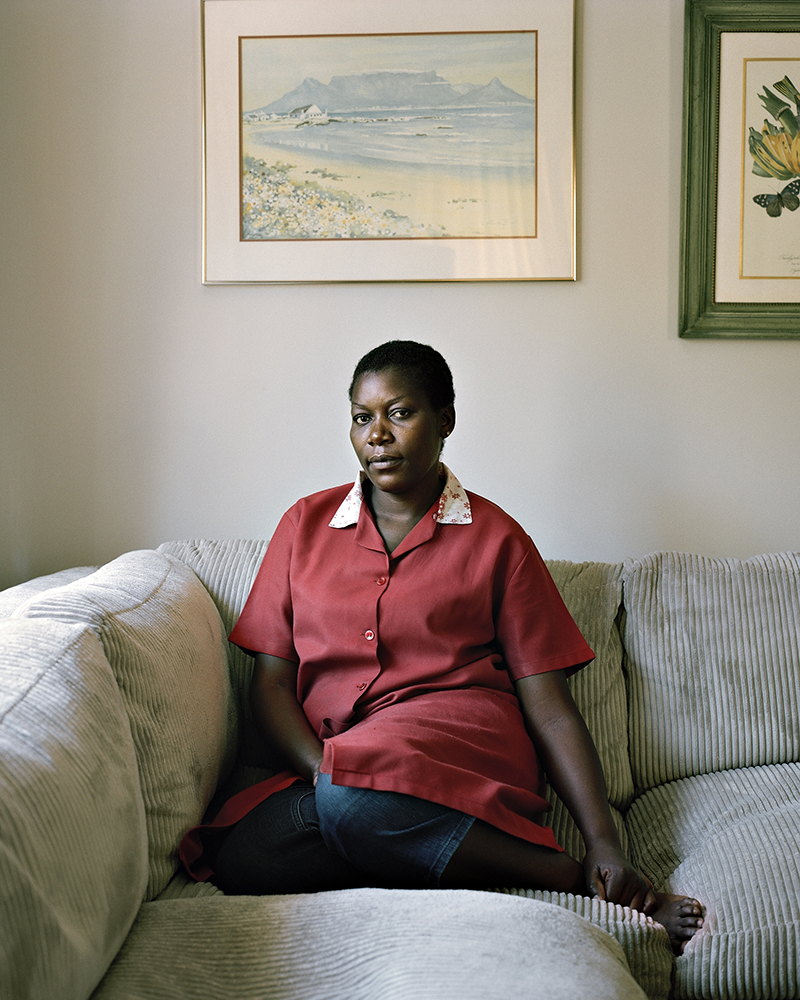
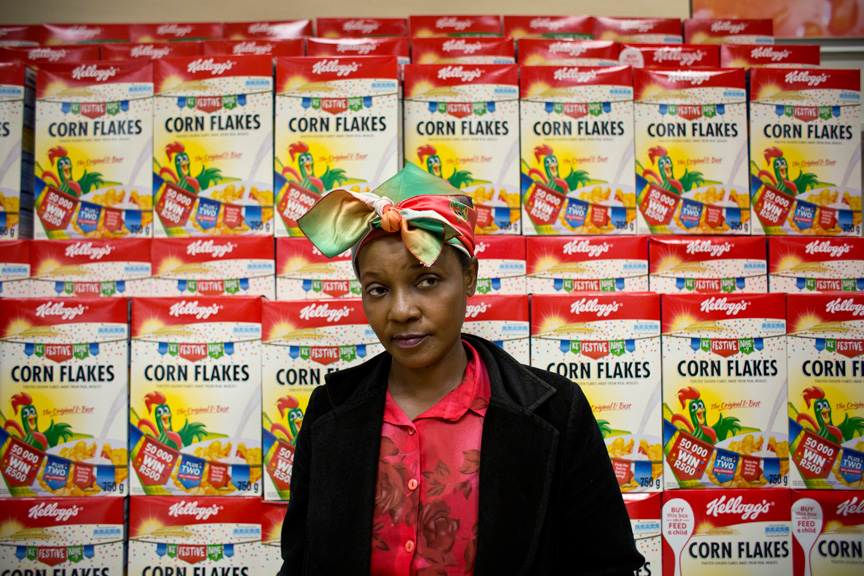
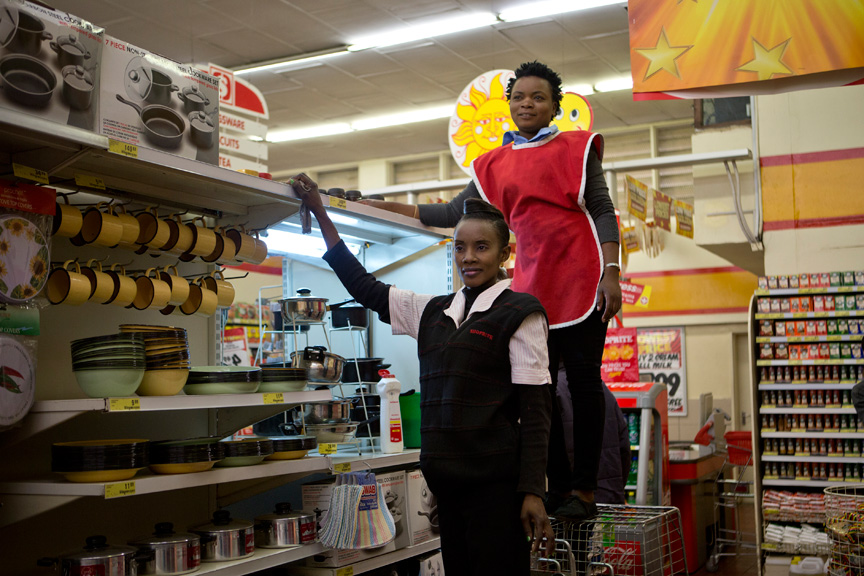
This can be seen in series’ such as Alice Mann’s Domestic Bliss (2014) which was met with public onslaught. The series depicted domestic workers dressed in uniform in the wealthy homes of their employers, not performing their daily tasks working for those homes, but instead in reclining poses on sofas and neatly made beds. They look uncomfortable, most of the time, sometimes even confrontational in their gaze. By creating a juxtaposed scene, that of the helpers in their uniforms on the one hand, and the luxury that surrounds them in their working situations on the other, the idea of an apparent “post” apartheid society is easily questionable. Against abundance and wealth, these women stand out as “other”.
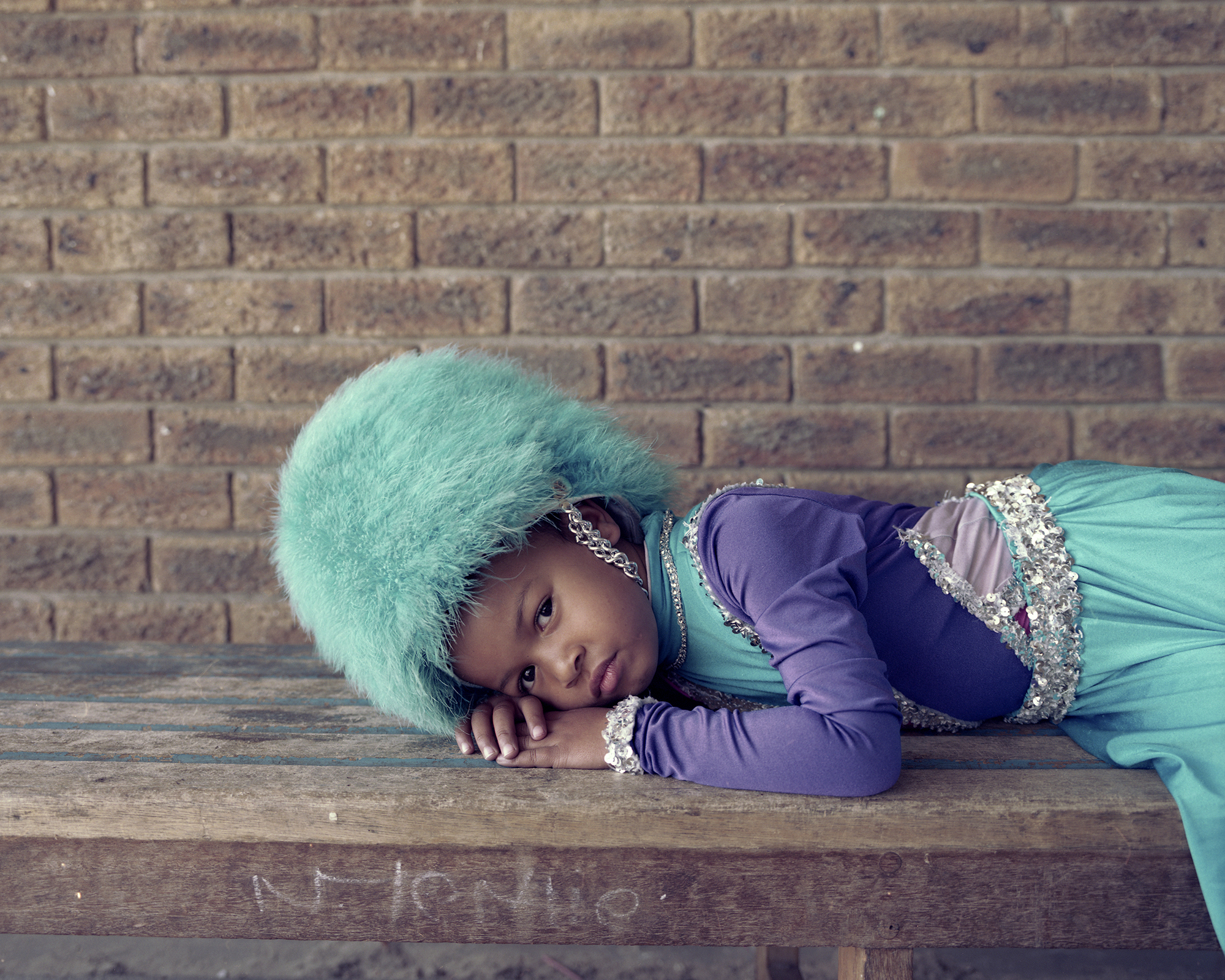
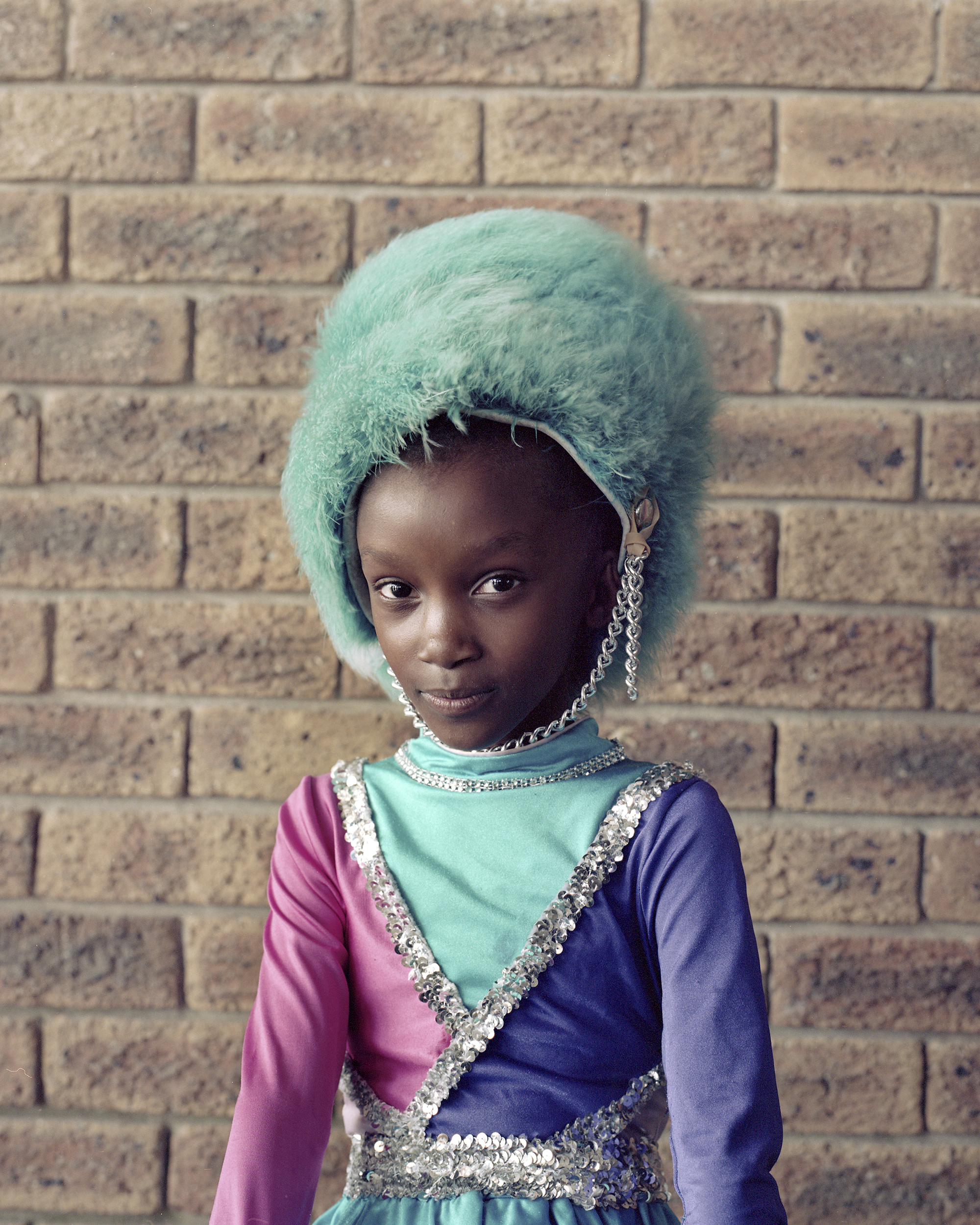
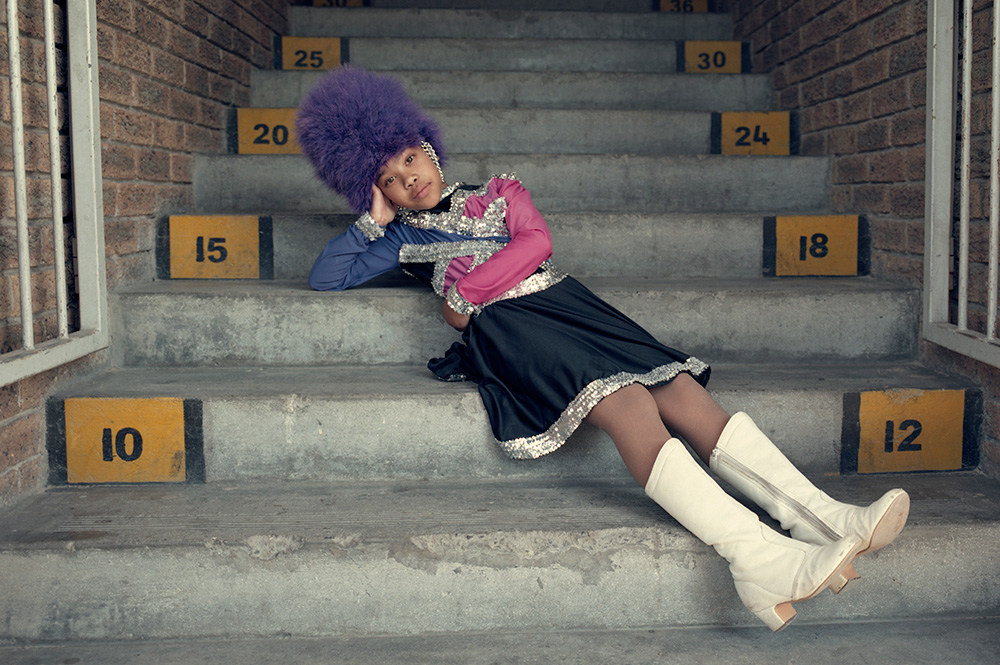
The white gaze continues into her photo essay Drum majorettes of Cape Town that focused on young primary school girls. They are seemingly unaware of how she is firstly, invasive, turning her lens on their family homes, their intimate spaces and changing their lives into a curiosity cabinet, a spectacle for people from all over the world to visually explore. And by extension, she makes their real-life experiences a commodity.

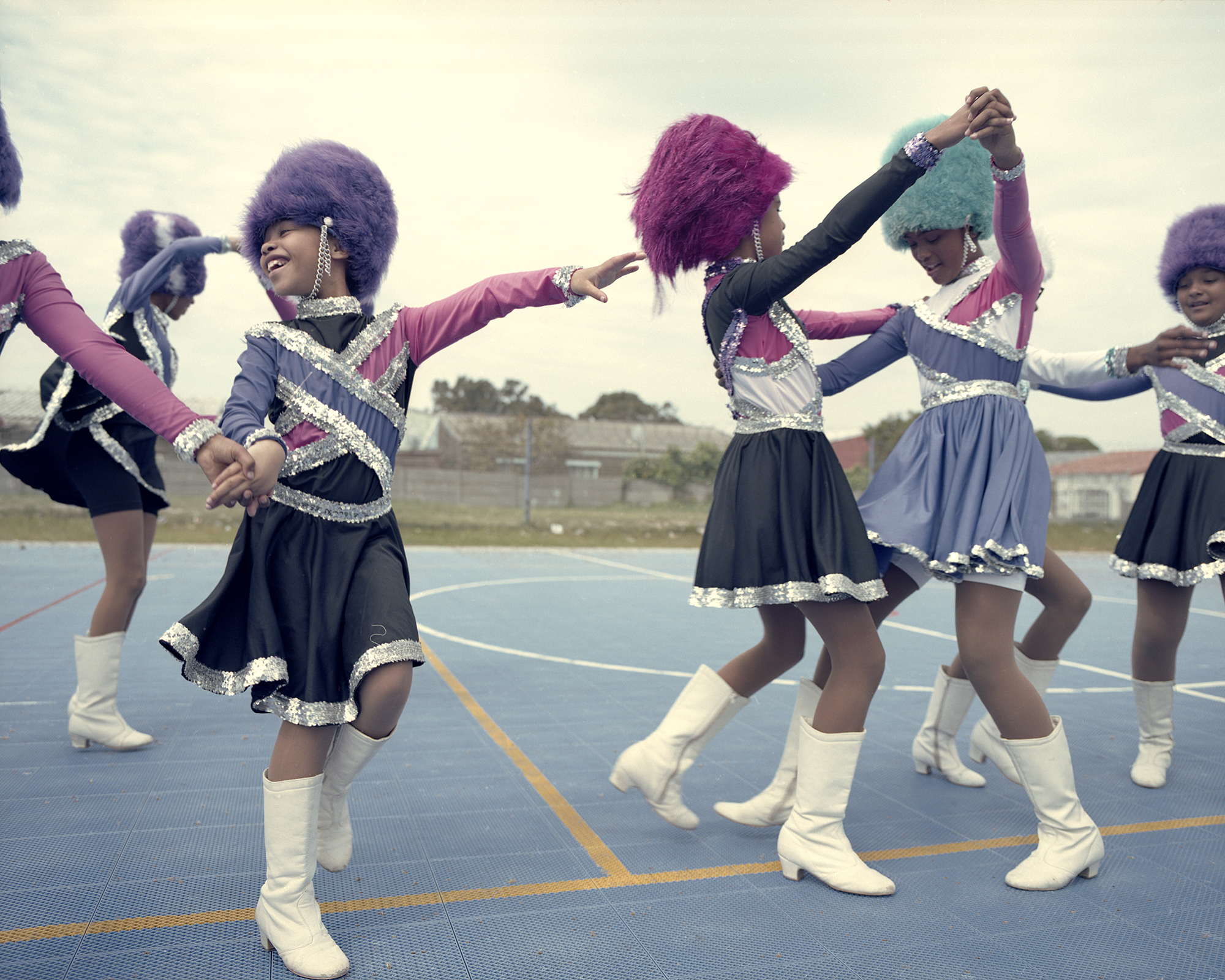
It might not be as visible in the Drum majorettes photo essay, but in Domestic Bliss it is almost all that stands out. The reason why I say this is because there cannot be anything more problematic than a white employer photographing her and her friends’ domestic workers to start off with. What’s more is that even though the helpers have consented to have these portraits taken of them, one can question how much choice they really had to reject this request.
These bodies of work speak of her subjectivity that she attempts to paint as ambiguity more than anything else. The mystery in Mann’s work lies in what they are suggesting about how her consensual models felt after she had photographed them (Sontag 1977: pg. 28). How did the woman and girls feel after they saw the portrayal of themselves in Mann’s eyes? Did they see themselves that way?
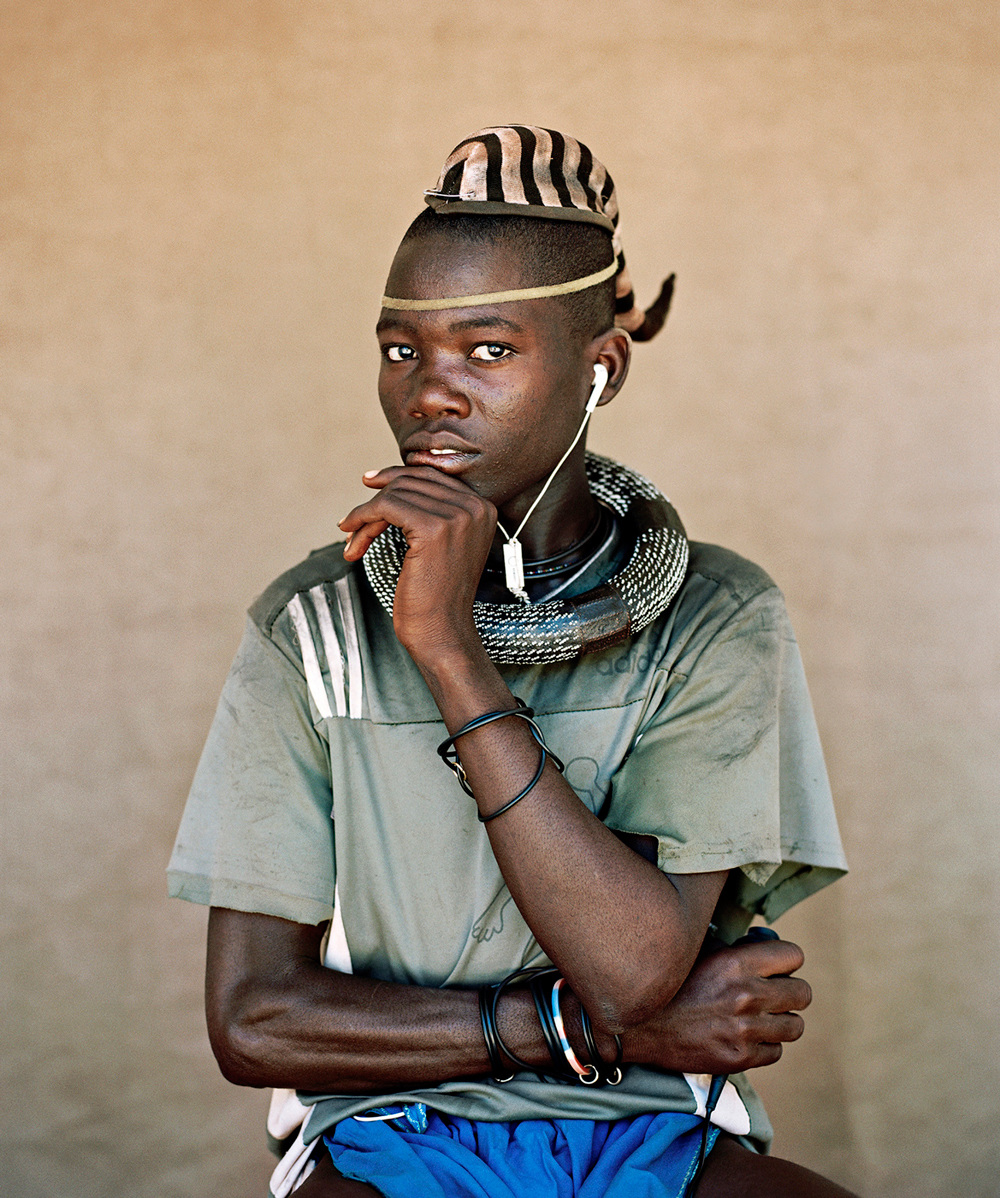
The white gaze is not something that can be spoken about impartially if only one white person’s work is being taken into account for such a discourse. Therefore, I next look at the work of Kyle Weeks. Weeks, born in Namibia, is known for his work that strikes the balance between portraiture and documentary depictions.
The problematic nature of his work lies in the “Asymmetrical power relations between whites and Blacks and the historical expansionist tendencies on the part of whites, and how they make themselves at home even when uninvited.” (Yancy, 2008: unknown page) This is again something that can be drawn to all three of the white photographers discussed in this piece. I am by no means stating that the white gaze is something that is exclusionary to the photographer’s discussed here, they merely serve as examples to aid in a difficult conversation.
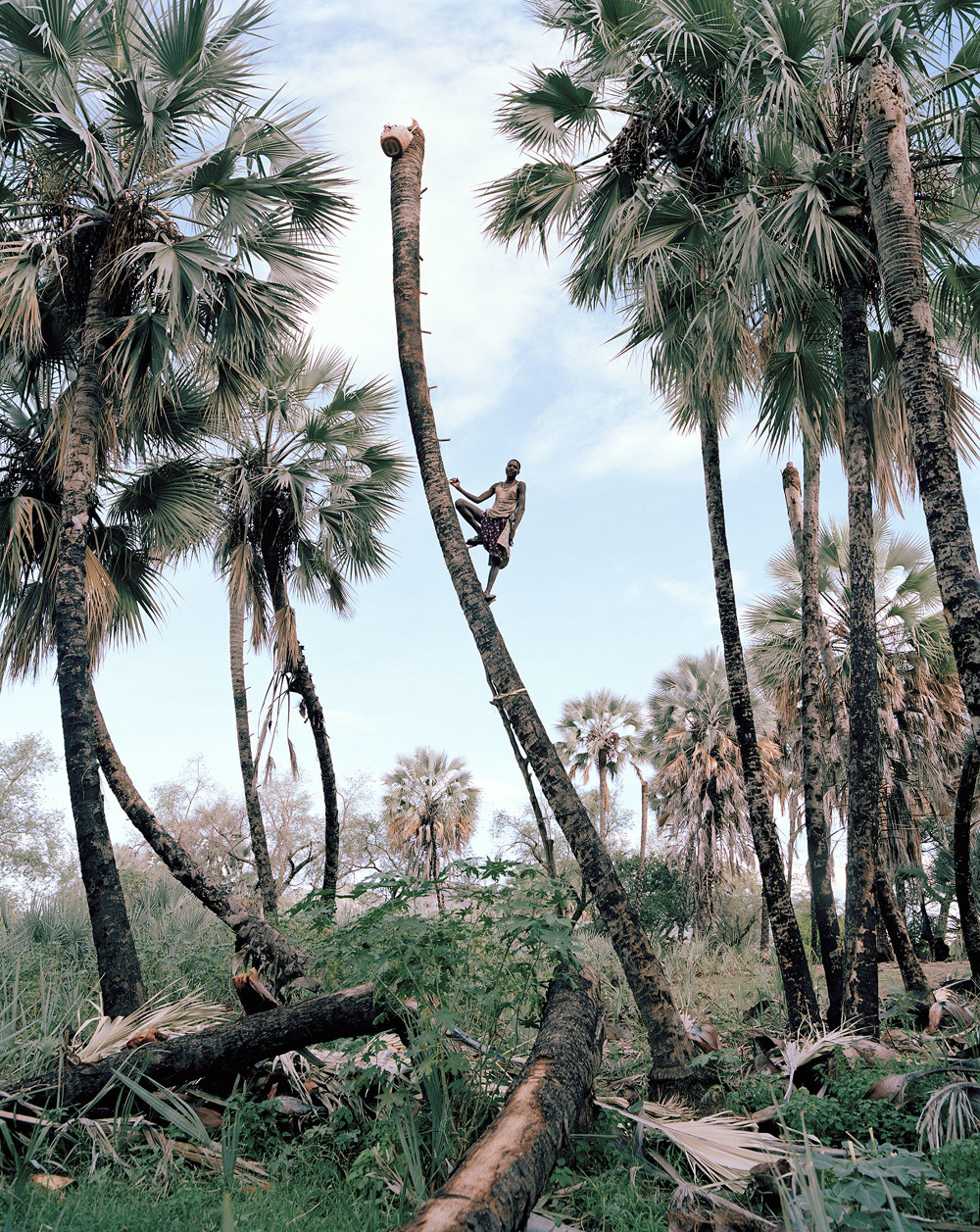
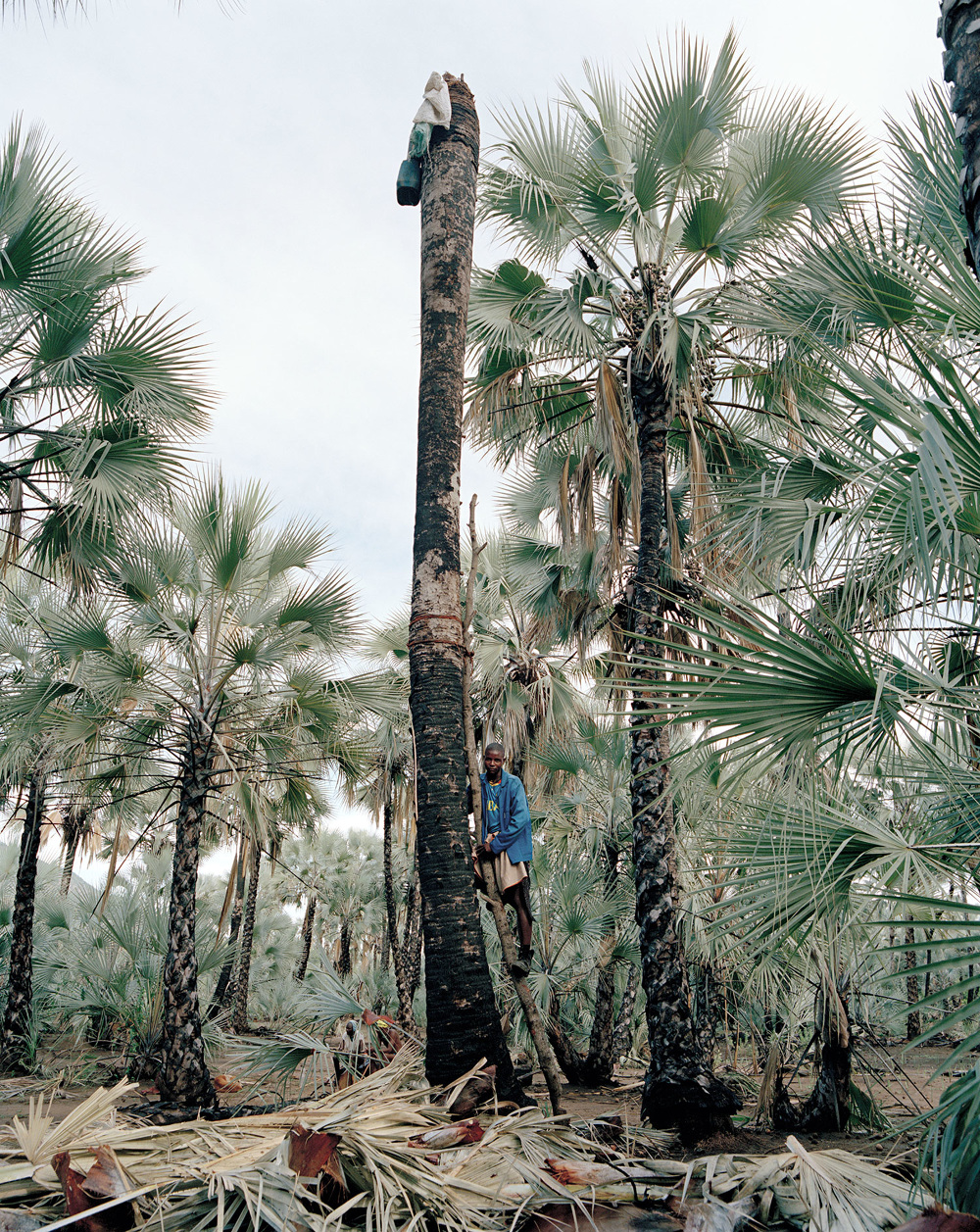


Weeks’ series, Palm Wine Collectors, visually explores the working lives and dynamics of the Makalani palm harvesters of northern Namibia in the Kunene Region. According to Week’s biography, this series offers, “a subversive alternative to voyeuristic documentary stylings.” Another body of work that can be put in the same category as the first is his portrait series, Ovahimba Youth Self-Portraits – a body of work that acts as a visual commentary on the longstanding colonial photographic methods used to depict Africans.”
My critique is the gaze of course but more than this the way in which these series’ are described by the visual auteur, and as Yancy states, the non-existent invitation that white people give themselves to lens the narratives of people of colour. To infiltrate their spaces without hesitation and to write narratives for people of colour however they deem fit.
Firstly, Weeks presents his Palm Wine Collectors series as a body of work that is progressive, as an alternative to voyeuristic documentary depictions. In my opinion, this body of work does not reflect objectivities and instead tells us more about Weeks as was the case with Mann. Both of Weeks’ bodies of work discussed here speak of subjectivities.
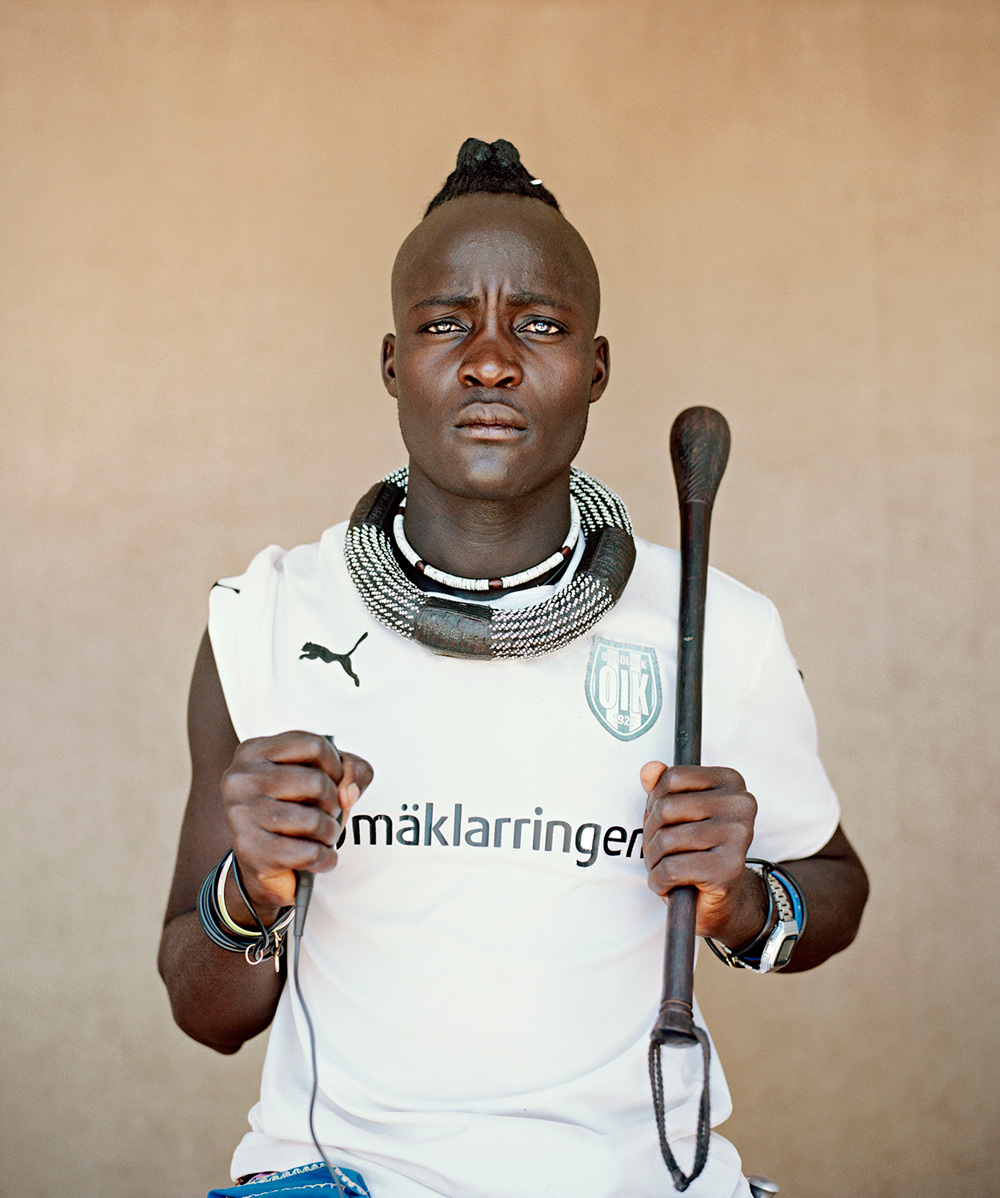
Ovahimba Youth Self-Portraits is aimed at subverting colonial photographic methods used to depict African people, and again by definition fails in this attempt and always will when lensed by a white individual who cannot acknowledge the effect of their whiteness. Weeks’ whiteness goes unnamed in his work.

The voices of racists declare themselves to be raceless; hidden behind the veneer of white “progressive liberalism”. By many white people, racism is understood in terms of white supremacy and white extremism and they fail to see their own acts of micro racism as they believe that their liberalism lends them as raceless and blameless. The privileged status of normative “absence” is given to the white body.
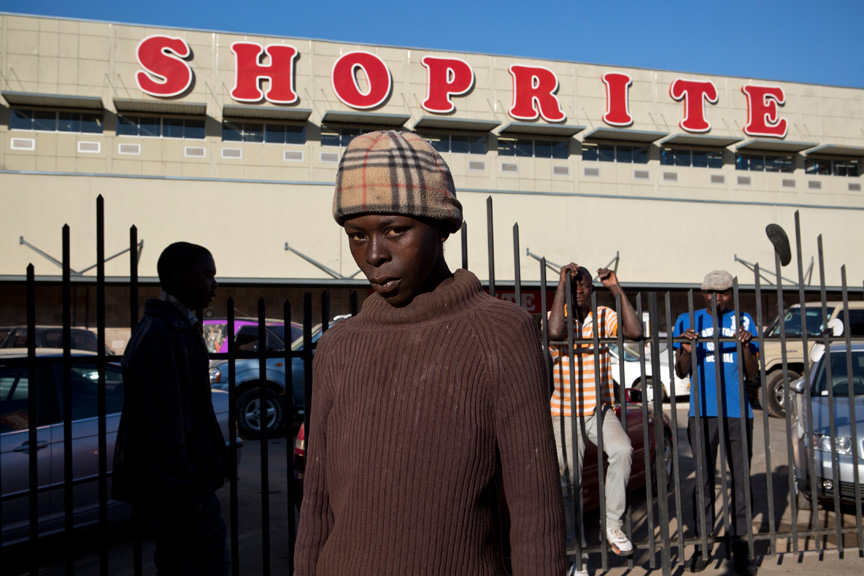
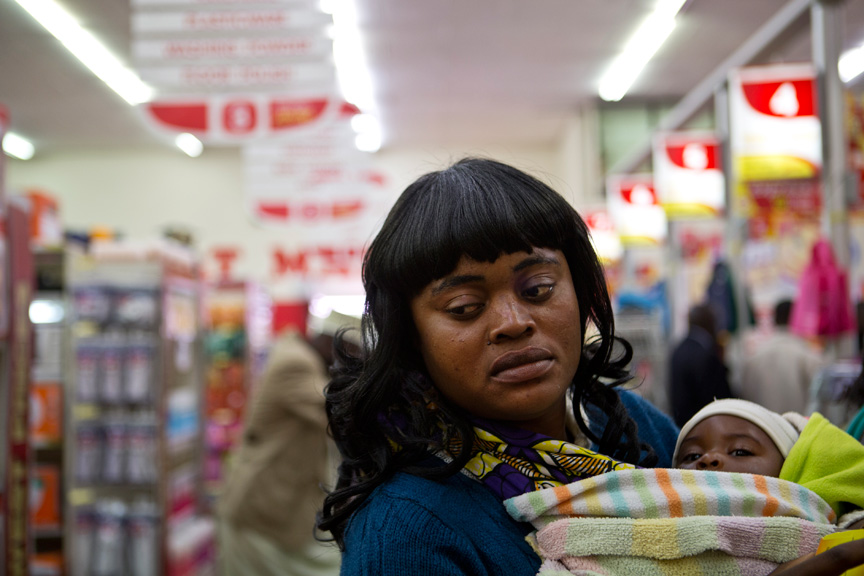
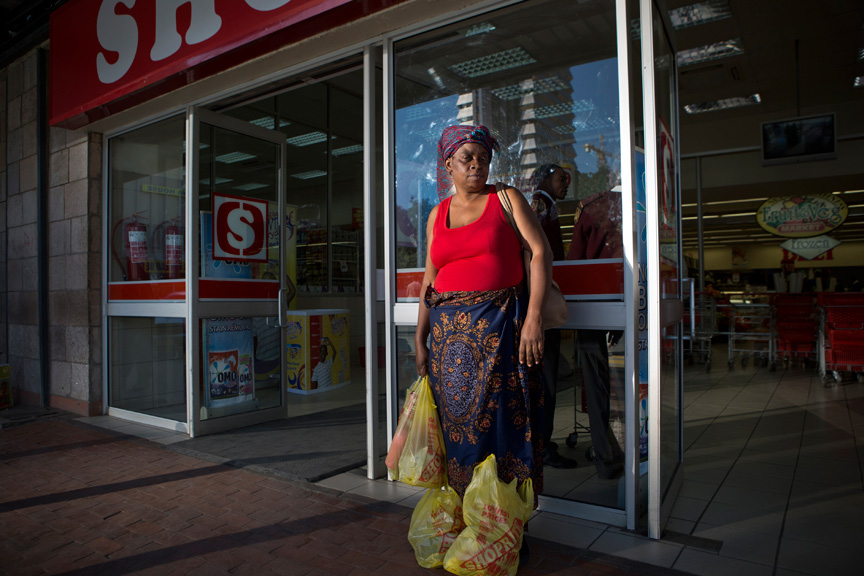
Alexia Webster’s work cannot be seen apart from the scope of the performers of the white gaze. It can be seen in bodies of work such as The Spread of the South African Supermarket – Portraits of Zambian Shoppers. The photo essay tells the story of the rise of the South African supermarkets in Zambia by photographing shoppers of colour in the act of shopping in a Shoprite chain store. Given, this was an assignment by the Financial Times Weekend magazine I still believe that objectivity is not prevalent and that this is a subjective body of work.
As with Mann’s photographic work, this body of work feels extremely invasive. Webster photographs people in the relatively private act of shopping; shopping is private for me at least and I would not enjoy being lensed while buying my supply of fresh food and other necessities. It is the white person’s assumed right to insert themselves into narratives they don’t understand and then even more than that; to convey the narrative, however, they see fit.
“The production of the Black body is an effect of the discursive and epistemic structuring of white gazing and other white modes of anti-Black performance. And while these performances are not always enacted consciously but the result of years of white racism calcified and habituated within the bodily repertoire of whites, whites are not exempt from taking responsibility for the historical continuation of white racism.” (Yancy, 2008: unknown page)


White solipsism arranges the world as a white space where “whiteness” is seen as a normal and universal condition. All three of the photographers discussed above fail to employ self-reflexivity with regard to how they positioned themselves as white photographers or how the ideology of whiteness positions them as “race-free”. Their apparent documentary work is simply an act of performing whiteness. What reinforces the status of whiteness is to allow it the power to go unnamed and to accept its status as a natural site of the human condition, thereby stripping people of colour of their humanity. Racialized meaning is re-established through silence.
“Becoming white” is different from being “phenotypically white” (Yancy, 2008: unknown page. Becoming white” then, is an additional layer or classification and refers to more than phenotypic markers. As Marilyn Frye states, being “whitely” is a deeply embedded way of being in the world (Frye, as sited in Yancy, 2008). Whiteness is performing both the phenotypic as well as a subjectivity that is structured by particular white epistemic orientations. Whiteness relates to one’s position in a white racist social structure that grants privilege.
In no way do the above statements negate that white people have different investments in whiteness, nor that there are white people who participate in antiracist forms of praxis. Despite this, however, white people continue to benefit from being phenotypically white irrespective of good intentions. White South Africans reap benefits from a previous hegemonic structure of hate built on white supremacy. I do not deny that white people have privilege by racism while are targets of classism, sexism, homophobia or ageism. I also do not deny that white people are beneficiaries of whiteness in different ways.

“In the process of naming their whiteness, whites must understand their role in a normalizing whiteness and also understand how whiteness is a site that is dutifully maintained.” (Yancy, 2008: unknown page) In the examples of the photographers mentioned leaving their whiteness unnamed and unidentified, has the effect of interposing Blackness as marked and the “real” object of their gaze. Whiteness, however, maintained its unmarked status and provided them with the latitude to create distance between themselves and white racists.
It is important for all people to understand the white gaze. To identify it, to confront it. White people need to be more self-reflexive of the way they are in the world and realize that racism isn’t something that is singular to white extremists but that small acts can as easily be a performance of the white gaze. White people need to stop inserting themselves into narratives that they do not belong in and make way for people of colour to tell their own stories. True objectivity is unattainable, especially with a camera.
“Critical reflections on whiteness should not begin and end with critical reflections on white supremacy. What is important is that the critical project of making seen the unseen of white privilege in mundane contexts is a significant endeavour that transcends unambiguous cases of white supremacy.” (Yancy, 2008: unknown page)





